Defining Your Internet Marketing Strategy
In the ever-online world of today, it needs to be said that every business must be online — no matter what type of business. If your business isn’t online, where have you been?! Have you been living under a rock?
Defining your Internet marketing strategy is as easy as 1, 2, 3 — as I have three general methods of determining how you should deploy Internet marketing and technology in your business.
The Internet as a Channel
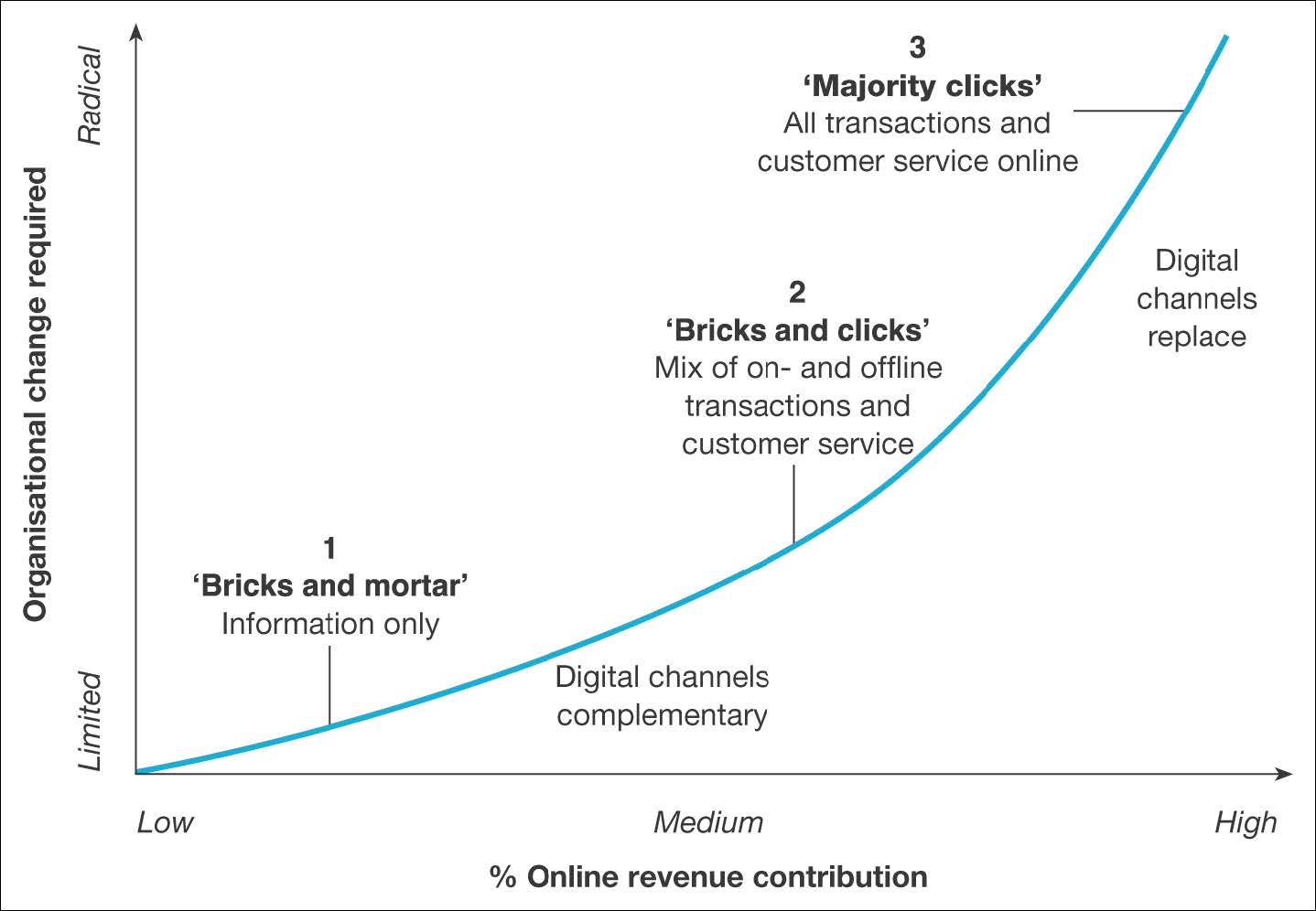
There are three main business models involved in this simple strategy: ‘Bricks and Mortar’, ‘Bricks and Clicks’, and ‘Majority Clicks’.
| Type | Description | Useful for | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bricks and Mortar | The website contains only information. | Businesses that don’t need to transact or communicate with customers online. | - Restaurants - Cafés - Fast food restaurants - Tradesmen |
| Bricks and Clicks | The website contains a mix of on- and offline transactions and customer service. | Businesses that have physical stores as well as transact or communicate with customers online. | - Retail stores - Pizza restaurants |
| Majority Clicks | The website contains all transactions and customer service online. | Businesses that only deal with customers online. | - Online platforms or software - E-Commerce - Crucial |
The three business models are different and are all distinct, but they are definitely not separate — they can be a process of evolution or progress for a business. Don’t ever feel like you’re stuck in a certain business model because it works well, you may just find that progressing to a different model may be a decision that works amazingly!
Here is a simple diagram to clarify how online revenue contribution from the Internet relates to the organisational change of a business:
As you can see, the higher the percentage of online revenue contribution, the more that the organisation needs to be online. It’s as simple as that!
Level of Commitments to E-Business
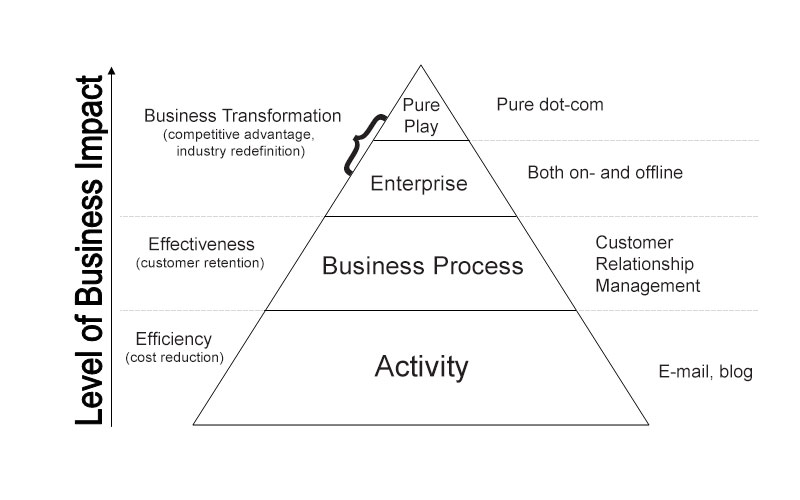
This strategy can best be explained through the use of a pyramid diagram:
Each level of the pyramid indicates a number of opportunities for the business to provide customer value and generate revenue using IT. Because there is no single classification of e-business models, we can categorise the most commonly used models
We can see that the level of business impact or commitments to E-Business defines what type of strategy that a business can pursue. For example, if a business is using E-Marketing as a business process — i.e. for customer retention — they can seek to focus on and utilise Customer Relationships Management (CRM).
Or, if a business is experiencing a stage of transformation or significant growth, they are moving into an enterprise model or pure play model (depending on the type of business), which can involve the business adopting a bricks and clicks or pure dot-com strategy, respectively.
5 Ss of Internet Marketing
The 5 Ss of Internet Marketing, from Emarketing Excellence: The Heart of eBusiness, are a benefits-based model that you can use to better strategise your Internet marketing. This model is probably the most comprehensible of the three models, as it includes 5 simple rules to follow when deploying Internet marketing for your business.
Sell — Grow sales
- Create promotions, show your best products, advertise, attract, sell, sell, sell!
Speak — Engage with consumers
- Customers like being communicated with and interacted with, it makes them feel recognised and valued; great ways to do this include: social media, competitions, etc.
Serve — Add value
- Adding customer-perceived value should be regular for a business. This involves creating loyalty/rewards programs, customer clubs, sales promotions, and so on.
Save — Save costs
- You should be looking to reduce costs of traditional (brick and mortar) processes in the business, e.g. printing.
Sizzle — Extend the brand online
- Add new products/services or features to your list, so you can branch out into other streams of revenue and customer engagement. Examples include clothes, footwear, desk accessories, Visa cards, figurines, or anything brand-able!